
Mongoose Cheat Sheet
mongoose
If you’re working with Mongoose, the popular object data modeling (ODM) library for MongoDB in Node.js, having a quick reference guide or “cheat sheet” can be incredibly helpful. In this blog post, we provide a concise summary of some of the most commonly used Mongoose methods and syntax, organized by category, to help you work more efficiently and effectively with this powerful ODM.
Schema definition
const { Schema } = require('mongoose');
const userSchema = new Schema({
name: String,
email: { type: String, unique: true },
age: Number,
isAdmin: { type: Boolean, default: false },
createdAt: { type: Date, default: Date.now }
});
Model definition
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const userSchema = require('./userSchema');
const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema);
Creating a document
const user = new User({
name: 'John Doe',
email: '[email protected]',
age: 30
});
user.save();
Finding documents
// Find all documents
const users = await User.find();
// Find documents that match a query
const admins = await User.find({ isAdmin: true });
// Find a single document by ID
const user = await User.findById(userId);
Updating documents
// Update a single document by ID
await User.findByIdAndUpdate(userId, { name: 'Jane Doe' });
// Update multiple documents that match a query
await User.updateMany({ isAdmin: true }, { isAdmin: false });
Deleting documents
// Delete a single document by ID
await User.findByIdAndDelete(userId);
// Delete multiple documents that match a query
await User.deleteMany({ isAdmin: false });
Validation
const userSchema = new Schema({
name: { type: String, required: true },
email: { type: String, required: true, unique: true },
age: { type: Number, min: 18 },
isAdmin: { type: Boolean, default: false },
createdAt: { type: Date, default: Date.now }
});
In Mongoose, you can define relationships between models using references or subdocuments.
Using references:
To define a relationship between two models using references, you can use the ref property in a field definition. The ref property specifies the name of the target model. Here’s an example:
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
posts: [{
type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,
ref: 'Post'
}]
});
const postSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: String,
content: String,
author: {
type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,
ref: 'User'
}
});
In this example, we have two models: User and Post. The User model has a field called posts, which is an array of ObjectId values that reference Postdocuments. The Post model has a field called author, which is an ObjectIdvalue that references a User document.
To populate the posts field of a User document with the corresponding Post documents, you can use the populate() function:
const user = await User.findById(userId).populate('posts');
This will retrieve the User document with the specified _id value and then retrieve the Post subdocument with the specified postId value.

> Written by
Emdadul Islam
Software Engineer. View profile →
Read more
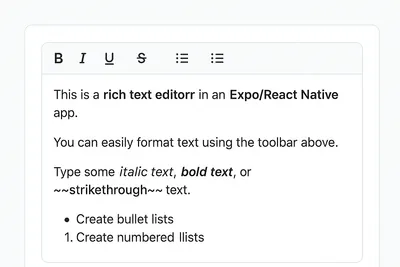
How to Add a Native Rich Text Editor in Expo / React Native (No WebView)
Rich text editing in React Native has always been tricky — especially when you want native performance instead of relying on WebViews. Most available libraries work great for the web, but fall short on mobile. That’s where [expo-rte](https://github.c...

How to Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) with TOTP in Your Web Application
In today’s digital landscape, securing user accounts with just a password isn’t enough. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an essential layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors. In this comprehensive guide,...

Host Your Own S3-Compatible MinIO Server on a VPS with Caddy and HTTPS
Host Your Own S3-Compatible MinIO Server on a VPS with Caddy and HTTPS Want to self-host object storage like AWS S3 but on your own VPS? Say hello to MinIO — a blazing-fast, S3-compatible storage solution. In this guide, we’ll show you how to install...