Exploring the Most Used Linux Commands with Examples
Photo by Gabriel Heinzer on Unsplash
Introduction:
Linux, with its powerful command-line interface (CLI), is a favorite among developers, system administrators, and enthusiasts alike. It offers a plethora of commands that make it a versatile and efficient operating system. In this article, we’ll dive into some of the most commonly used Linux commands, providing examples to help you understand their functionality and usefulness.
1. ls — List Directory Contents
The ls command is the go-to tool for listing the contents of a directory. By default, it displays files and directories in the current directory.
Example:
$ ls
2. cd — Change Directory
cd is used to change the current working directory. It allows you to navigate through the file system.
Example:
$ cd /path/to/directory
3. pwd — Print Working Directory
To know your current location in the file system, use the `pwd` command.
Example:
$ pwd
4. mkdir — Create Directory
Need to create a new directory? Use mkdir.
Example:
$ mkdir new_directory
5. rm — Remove Files and Directories
rm is used for deleting files and directories. Be cautious with this command, as it can lead to irreversible data loss.
Example:
$ rm file.txt
$ rm -r directory/
6. cp — Copy Files and Directories
Use cp to copy files and directories.
Example:
$ cp file.txt new_file.txt
$ cp -r directory/ new_directory/
7. mv — Move or Rename Files and Directories
mv is used for moving files and directories. It can also rename files and directories.
Example:
$ mv old_file.txt new_location/
$ mv old_name.txt new_name.txt
8. touch — Create Empty Files
Create an empty file using the touch command.
Example:
$ touch new_file.txt
9. cat — Concatenate and Display File Contents
cat displays the contents of a file on the terminal.
Example:
$ cat file.txt
10. grep — Search Text Using Patterns
grep is a powerful tool for searching text within files using patterns.
Example:
$ grep “search_term” file.txt
11.ps — Display Information about Running Processes
`ps` shows information about the current running processes.
Example:
$ ps aux
12. kill — Terminate Processes
Use kill to terminate processes by their process ID (PID).
Example:
$ kill -9 PID
13. df — Display Disk Space Usage
df provides information about disk space usage on your system.
Example:
$ df -h
14. du — Display Directory/File Space Usage
du displays the space usage of directories and files.
Example:
$ du -sh directory/
15. chmod — Change File Permissions
chmod is used to change file permissions.
Example:
$ chmod 755 file.sh
Conclusion
These are just a few of the most commonly used Linux commands. Familiarizing yourself with these commands and their usage will greatly enhance your ability to work efficiently on a Linux system. As you become more proficient with the Linux CLI, you’ll discover countless other commands that can help you perform various tasks and manage your system effectively. So, keep exploring and mastering the Linux command-line interface to become a proficient Linux user.

> Written by
Emdadul Islam
Software Engineer. View profile →
Read more
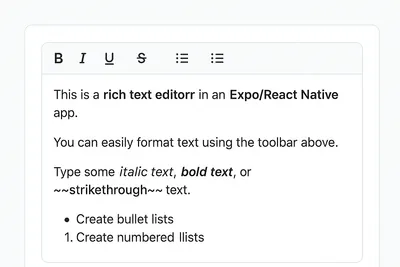
How to Add a Native Rich Text Editor in Expo / React Native (No WebView)
Rich text editing in React Native has always been tricky — especially when you want native performance instead of relying on WebViews. Most available libraries work great for the web, but fall short on mobile. That’s where [expo-rte](https://github.c...

How to Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) with TOTP in Your Web Application
In today’s digital landscape, securing user accounts with just a password isn’t enough. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an essential layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors. In this comprehensive guide,...

Host Your Own S3-Compatible MinIO Server on a VPS with Caddy and HTTPS
Host Your Own S3-Compatible MinIO Server on a VPS with Caddy and HTTPS Want to self-host object storage like AWS S3 but on your own VPS? Say hello to MinIO — a blazing-fast, S3-compatible storage solution. In this guide, we’ll show you how to install...